The secret behind the world’s most successful brands is the seamless coordination of the seven marketing functions. Businesses that master these seven functions position themselves not just to win customers, but to keep them loyal. But what are they exactly? Keep reading to learn more!
In This Article:
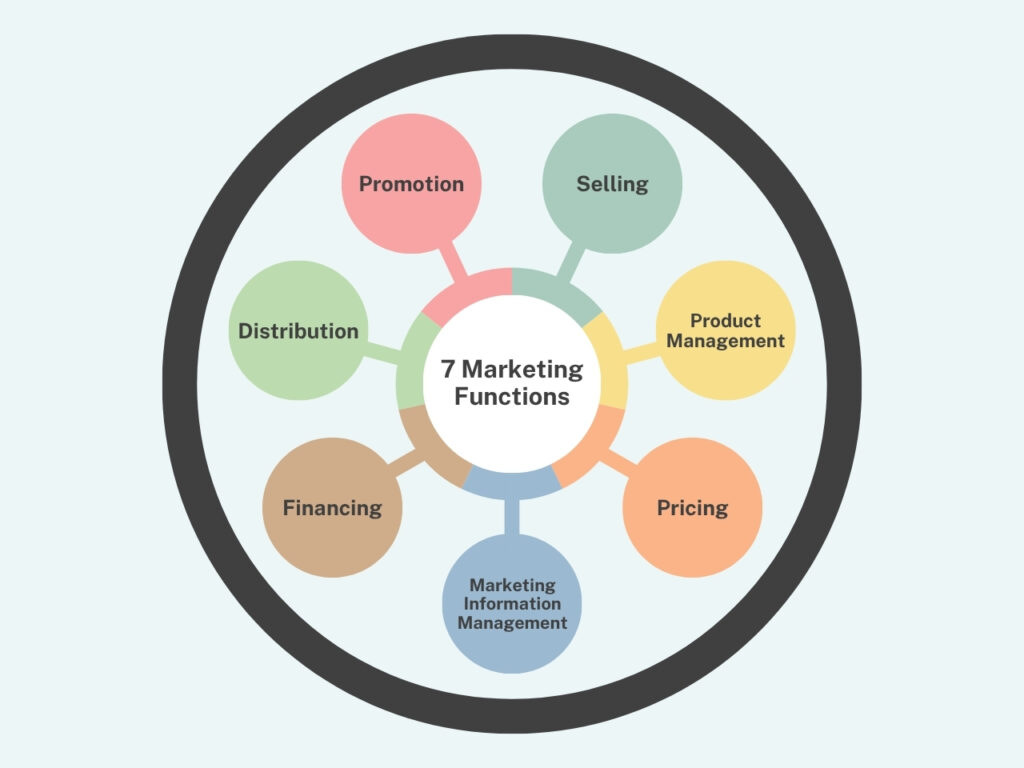
What Are The 7 Functions Of Marketing?
Promotion
Promotion is the process of making potential customers aware of a product or service and persuading them to take action. It includes advertising, social media campaigns, email marketing, influencer partnerships, events, and public relations. Effective promotion fosters brand awareness, builds credibility, and drives interest.
For example, 35% of companies that use email marketing generate an average ROI of $10 to $36 for every $1 spent (Litmus, 2025). Similarly, influencer marketing has grown into a $24 billion industry by 2024, reflecting its power to reach the target audience.

Promotion strategies must be tailored to specific customer segments. For instance, TikTok ads resonate strongly with Gen Z, while LinkedIn campaigns are more effective for B2B outreach.
Promotion doesn’t exist in isolation. It depends on product quality, pricing, and distribution. A well-executed promotional strategy ensures a brand stays visible in competitive markets and turns awareness into tangible sales opportunities.
Selling
Selling is about converting interest into transactions by nurturing relationships and addressing customer needs. Unlike pure advertising, selling involves one-to-one or personalized engagement, such as direct sales calls, in-store consultations, or digital chat support. The goal is not only to persuade customers to purchase but also to build long-term loyalty.
Selling strategies often align closely with the customer journey: awareness, consideration, and decision-making. Techniques may include offering demos, handling objections, or providing limited-time offers to close deals. In B2B marketing, strong selling strategies reduce churn and improve client lifetime value.
Statistics show that improving customer retention by just 5% can increase profits by 25–95% (Harvard Business Review). Selling integrates with other functions like pricing and promotion to ensure a seamless buying experience, ultimately distinguishing a brand from its competitors.
Product and Service Management
Product and service management involves developing, improving, and refining offerings to meet customer needs and stay competitive. This function spans concept design, product lifecycle management, feedback analysis, and cross-department collaboration.
For example, Apple’s annual iPhone updates demonstrate how consistent innovation sustains customer interest while addressing market demands. Market research plays a pivotal role.
42% of startups fail because there is no market need for their product (Forbes, 2024). By analyzing competitors, gathering customer feedback, and monitoring trends, businesses can avoid this pitfall. Product management also influences branding.
For instance, eco-friendly packaging aligns with sustainability-focused consumers, who account for 69% of global buyers (NIQ, 2023).
Marketers often work closely with R&D and operations teams to ensure that the product’s features, pricing, and delivery reflect customer expectations. Ultimately, effective product and service management ensures the business delivers value that matches or exceeds market demand.
Pricing

Pricing is more than assigning a dollar value; it reflects how customers perceive a product’s worth compared to alternatives. Successful pricing strategies consider production costs, competitor pricing, customer willingness to pay, and overall brand positioning.
For example, luxury brands like Hermès can price handbags at $10,000+, not because of production costs alone but due to perceived exclusivity and prestige. In contrast, discount retailers thrive by appealing to price-sensitive buyers.
Research shows that 59-60% of consumers say price is the main purchase driver, but perception of value often outweighs low cost (Medallia, 2025). Dynamic pricing, where prices adjust based on demand and competition, is used widely by airlines and e-commerce platforms like Amazon.
Mispricing can damage both profits and brand image. If too high, customers won’t buy; if too low, the brand risks being perceived as cheap. Therefore, pricing requires careful balance and continuous market monitoring.
Marketing Information Management

Marketing information management (MIM) refers to the systematic collection, analysis, and use of data to make better marketing decisions. This includes customer demographics, preferences, feedback, competitor activity, and market trends.
In today’s digital era, data is the cornerstone. Companies that leverage customer behavior insights outperform peers by 85% in sales growth (Forbes, 2023). Sources of information include surveys, online reviews, CRM systems, and social media engagement metrics.
For instance, analyzing website traffic can reveal which products are most appealing, guiding promotional efforts and inventory planning. Effective MIM also breaks down organizational silos by sharing data across departments, allowing product teams, sales, and finance to collaborate more strategically.
An example is Netflix, which uses viewing data to decide what shows to produce, resulting in globally popular hits like Stranger Things. Ultimately, strong MIM ensures decisions are data-driven rather than intuitive, reducing risk and improving ROI across all marketing activities.
Financing
Financing in marketing refers to securing and managing the funds necessary to design, execute, and scale campaigns. This can involve budgeting within the company, attracting investors, or proving ROI to secure more resources. Marketing often competes with other departments for limited funding, so demonstrating impact is essential.
According to ChatterBuzz, companies that allocate 11% of their annual budget to marketing grow 2.5 times faster than peers who spend less. Financing also extends to helping customers afford products, such as offering installment plans, credit, or subscription models.
Peloton, for example, grew rapidly by combining premium equipment with financing options. A strong financing strategy ensures that marketing activities don’t just start strong but can be sustained over time.
Moreover, securing funds for innovative strategies like AI-driven personalization or influencer partnerships allows companies to stay competitive. Without financing, even the most creative marketing ideas remain unexecuted.
Distribution

Distribution ensures that products and services are delivered to customers through the most efficient and appropriate distribution channels. This may include retail outlets, wholesalers, direct sales, e-commerce platforms, or hybrid models.
Effective distribution aligns with customer expectations. Statistics show that 63% of consumers expect free two-day shipping, making logistics a central marketing concern (Red Stag Fulfillment, 2025).
Poor distribution can undermine successful campaigns, as seen in Popeye’s 2019 chicken sandwich launch, where viral promotion led to overwhelming demand that outstripped supply, frustrating customers.
On the flip side, Amazon’s distribution network sets a global benchmark: its Prime program has about 220 million subscribers worldwide, largely due to its seamless logistics.
Distribution strategies must also adapt to digital transformation. For example, D2C (direct-to-consumer) models allow brands like Warby Parker to bypass middlemen and strengthen customer relationships. Ultimately, distribution is the bridge between marketing promises and customer satisfaction, ensuring that what is promoted is reliably delivered.
Why These 7 Marketing Functions Are Important
The seven functions of marketing are essential because they ensure businesses operate as a cohesive system rather than isolated activities. Promotion creates awareness, selling builds trust, and distribution ensures delivery. Without any one of these, the customer experience breaks down.
Data shows that companies aligning all marketing functions experience 32% faster revenue growth compared to those with siloed departments (LinkedIn, 2025). Each function supports the others: pricing signals value, financing makes campaigns possible, product management ensures market relevance, and information management ties it all together with data.
Collectively, these functions form the backbone of customer-centric strategies. For example, Netflix combines product management (content selection), distribution (streaming), pricing (subscription tiers), and promotion (personalized recommendations) to dominate its industry.
The importance lies not just in execution, but in integration, treating marketing functions as interconnected gears that power business growth, customer satisfaction, and long-term brand equity.
Tips To Implement All The Marketing Functions
Follow these strategies to ensure all marketing functions work effectively:
- Take a holistic approach: The seven functions of marketing work best when they complement each other. Instead of treating them as separate silos, create integrated strategies where promotion, pricing, selling, and distribution reinforce one another.
- Base decisions on data: Use marketing information management to collect insights from surveys, analytics, and competitor research. Data-driven decision-making improves accuracy in pricing, targeting, and product development, reducing the risks of guesswork.
- Align cross-functional teams: Collaboration between marketing, sales, finance, and product management ensures smoother execution. To keep all functions aligned, many businesses rely on structured monthly workflows that help teams regularly review performance, budgets, and operational priorities. Shared KPIs and consistent communication across departments help every function support overall business objectives.
- Invest in continuous improvement: Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of campaigns, distribution methods, and pricing models. Small adjustments informed by feedback and market shifts often yield better results than one-time overhauls.
- Balance short-term and long-term goals: While promotions and sales drive immediate revenue, financing, product management, and brand positioning build sustainable growth. Allocate resources to both areas to maintain competitiveness.
- Focus on customer experience: From promotion to post-purchase support, every function should enhance the customer journey. Satisfied customers not only boost sales but also provide valuable feedback that fuels better products and marketing strategies.
How To Know Which Marketing Function Needs Improvement
Identifying weak points starts with tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) for each function. If sales conversions are low despite strong promotion, selling may need refinement. Poor distribution metrics, like delayed shipping or stockouts, signal logistics gaps.
Negative customer reviews about product features point to product management issues. If campaign ROI is unclear, marketing information management or financing may be the culprit. So, follow the data, listen to customers, and evaluate KPIs regularly to pinpoint which function requires improvement.