Cost Per Click (CPC) is one of the most important metrics in online advertising. It tells you exactly how much you pay each time someone clicks on your ad, making it a clear and actionable way to measure campaign costs.
Unlike CPM, where you pay for impressions, CPC ensures you only spend money when users take action. Knowing how to work out CPC gives you the insights you need to optimize campaigns. Keep scrolling down for more!
What is Cost Per Click?
Cost Per Click (CPC) is the amount you pay every time someone clicks on your online ad. Instead of paying for how many times your ad is shown, you only pay when a person takes action by clicking. This makes CPC a fair and clear way to measure how much your advertising is costing you.
CPC is important because it helps you control your budget and track results. By knowing your CPC, you can see if your ads are bringing in visitors at a good price. A lower CPC means you are reaching more people for less money, which helps improve your return on investment and grow your marketing success.
How To Calculate CPC
The Cost Per Click Formula
The most common way to calculate Cost Per Click (CPC) is straightforward:
CPC = Advertising Cost (Ad spend) / Number of Clicks
In which:
- Advertising cost: The total amount of money you spent on your ad campaign.
- Number of clicks: The total clicks your ads received.
CPC Calculator
This formula is the most direct method, as it tells you exactly how much each click costs based on your spending and results. You can use this formula to calculate the CPC in each marketing channel or measure the average CPC across all platforms.
An alternative formula combines CPM (Cost per Mille, or Cost per 1,000 impressions) and CTR (Click-Through Rate):
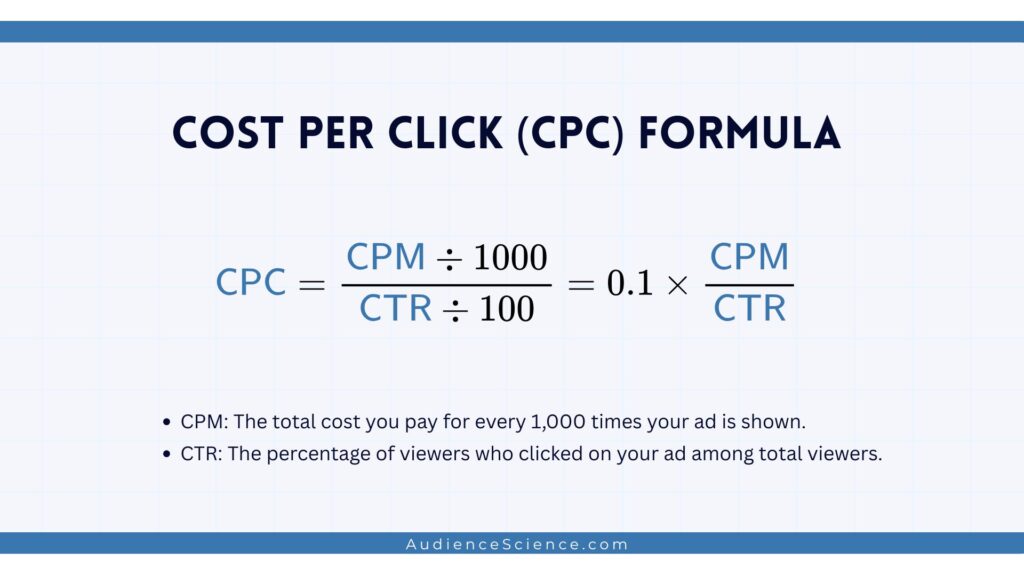
CPC = (CPM ÷ 1000) / (CTR ÷ 100) = 0.1 × CPM / CTR
In which:
- CPM: The total cost you pay for every 1,000 times your ad is shown.
- CTR: The percentage of viewers who clicked on your ad among total viewers.
To calculate CTR, use:
CTR = (Clicks / Impressions) × 100
This formula is helpful when you have data about impressions and click-through rates rather than total campaign cost and clicks.
Finally, when managing larger campaigns, you may want to know your average CPC:
Average CPC = Total Advertising Cost (Ad spend) / Total Clicks
This helps track overall efficiency across multiple ads, ad groups, or campaigns, giving a clearer picture of performance over time.
Example
Using the common formula:
Imagine you spend $200 on a Google Ads campaign and receive 100 clicks.
CPC = $200 ÷ 100 = $2 per click.
This means each visitor brought to your site through the ad costs you $2.
Using the alternative formula (CPM + CTR):
Suppose your CPM is $10 (you paid $10 for every 1,000 ad impressions), and your CTR is 2% (0.02).
CPC = 0.1 × CPM / CTR = 0.1 × 10 / 0.02 = 1 / 0.02 = $50 per click.
This shows how combining CPM and CTR can give you a different perspective on the total cost. In this case, although the ad reached many people, a low CTR made each actual click more expensive.
FAQs
What is a good CPC?
A “good” CPC depends on your industry, competition, and campaign goals. On average, CPC rates for Google Ads are about $2.69 for search ads and $0.63 for display ads. If your CPC is around or below these benchmarks, it’s generally considered good.
However, a truly good CPC is one that delivers profitable traffic, meaning the cost per click is low enough to generate a positive return on investment (ROI).
What is the difference between CPC and CPM?
Both CPC and CPM are commonly used by advertisers, but they are not the same:
- Cost Per Click (CPC): You pay whenever someone clicks on your ad. It’s best for campaigns focused on driving traffic, leads, or conversions.
- Cost Per Mille (CPM): You pay for every 1,000 times your ad is shown, no matter if people click or not. It’s mainly used for brand awareness and visibility.
The choice depends on your goal. CPC works when you want measurable actions, while CPM is better for reaching large audiences.
What affects CPC?
CPC is influenced by factors like your maximum bid, ad quality score, and ad rank. Competition for keywords, especially generic ones, can raise costs, while niche or branded terms are cheaper. Platform choice and campaign context, such as audience targeting, also affect CPC.
How to optimize CPC?
To optimize CPC, focus on improving ad relevance and quality score, as higher-quality ads often cost less per click. Use targeted keywords, refine audience settings, and test different ad creatives and ad placements. Lower bids on low-performing keywords and prioritize those with better ROI to maximize efficiency and reduce costs.
See more marketing calculator tools: