Ever wondered if you’re paying too much to get your ads seen? That’s where CPM (Cost per Mille) comes in. This simple metric reveals how much you spend for every 1,000 ad impressions, helping you judge whether your campaigns are truly cost-effective.
With a quick cost per thousand calculator, you can compare platforms, spot savings opportunities, and make sure your budget is working harder for your brand. Explore more about this metric below!
What is CPM?
CPM stands for Cost per Mille, which means the total cost an advertiser pays for every 1,000 times an ad is shown, also called impressions. The “M” comes from the Latin word mille, meaning one thousand. So, you might also call it “cost per 1,000 impressions.” CPM is one of the most common ways to price ads online because it is simple and easy to understand for both advertisers and publishers.
Here’s how it works: every time an ad appears on a screen, it counts as an impression. Advertisers are charged based on how many thousands of impressions their ad gets, not whether people click or take action. For example, if a CPM is $5, the advertiser pays $5 for every 1,000 times the ad is displayed.
Calculating CPM is important for digital marketing because it helps advertisers measure the cost of reaching a target audience and compare the value of different campaigns or platforms. It also helps publishers and brands track visibility, plan advertising budgets, and improve ad strategies for better results.
How To Calculate CPM
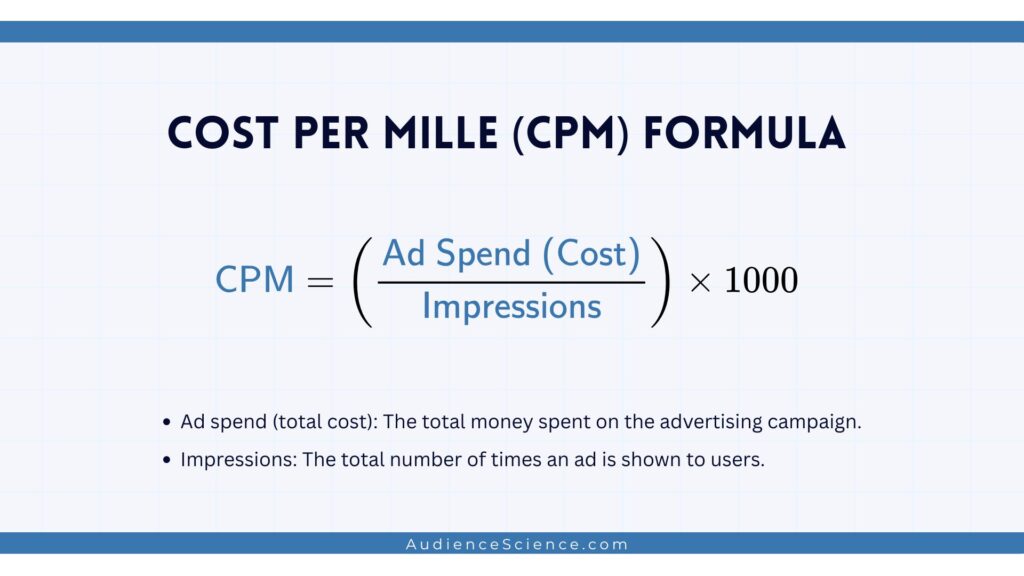
The CPM Formula
The formula for calculating CPM is:
CPM= (Ad Spend or Cost / Impressions) x 1,000
In which:
- Ad spend (total cost): The total money spent on the advertising campaign.
- Impressions: The total number of times an ad is shown to users.
- Why multiply by 1,000? Since CPM is measured per thousand impressions, multiplying by 1,000 standardizes the calculation.
CPM Calculator
Businesses can measure the CPM on multiple platforms and compare the effectiveness. With the same campaign budget, the channel with a lower CPM means you’re getting more visibility.
You can also rearrange the formula:
Cost = (CPM × Impressions) / 1000 -> to find how much you’ll spend.
Impressions = (Cost / CPM) × 1000 -> to find how many ad views your budget can buy.
This makes CPM useful for both advertisers planning budgets and publishers predicting revenue.
Example
Imagine you spend $500 on an ad campaign and your ad is shown 200,000 times.
CPM= (500 / 200,000) x 1000 = 2.5
So, the CPM is $2.50. This means you paid $2.50 for every 1,000 impressions.
FAQs
What is a good CPM?
A good CPM is usually considered to be lower than the industry average, because it means you are reaching more people at a lower cost. However, what counts as “good” can vary depending on the platform, audience quality, and campaign goals.
Here are the average CPM rates across popular platforms:
- Facebook: $7.19
- Instagram: $7.91
- YouTube: $9.68
- LinkedIn: $6.59
- X (Twitter): $6.46
- Pinterest: $30
Should I use CPM, CPC, or CPA?
The right model depends on your advertising campaign goal: visibility (CPM), traffic (CPC), or conversions (CPA).
- CPM (Cost per Mille): Best for brand awareness. You pay for impressions, not actions. Pros: simple and predictable. Cons: no guarantee of clicks or conversions.
- CPC (Cost per Click): Best for driving traffic. You only pay when someone clicks your ad. Pros: more direct engagement. Cons: clicks don’t always equal sales.
- CPA (Cost per Action): Best for conversions. You pay only when a user completes an action, like a purchase or signup. Pros: low risk for advertisers. Cons: risky for publishers who rely on advertiser performance.
How to optimize CPM?
Here are some tips you can apply to reduce the CPM:
- Choose strong ad networks like Google AdSense.
- Prepare for seasonal changes (e.g., higher CPM around holidays).
- Use a Supply Side Platform (SSP) to attract more advertisers.
- Improve ad placement and formats to increase visibility.
- Track metrics like eCPM, vCPM, and rCPM for deeper insights.
See more marketing calculator tools: